Difference between revisions of "ProjectsBlocks"
From Bioinformatics Core Wiki
Jponomarenko (Talk | contribs) |
Jponomarenko (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
| − | |Title=Lung | + | |Title=Lung Microbiomes of COPD Patients |
|Description=CRG collaborates with the Hospital San Pau, Hospital Clinic, Hospital del Mar and other institutions in Barcelona on studies of the lung micro biomes of patients affected by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The Bioinformatics Core is part contributes to the project by processing and analyzing of the sequencing data. | |Description=CRG collaborates with the Hospital San Pau, Hospital Clinic, Hospital del Mar and other institutions in Barcelona on studies of the lung micro biomes of patients affected by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The Bioinformatics Core is part contributes to the project by processing and analyzing of the sequencing data. | ||
|Color=rgba(198, 127, 157, 0.45) | |Color=rgba(198, 127, 157, 0.45) | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
|Title=AnnoWiki | |Title=AnnoWiki | ||
| − | |Description=AnnoWiki is a Semantic MediaWiki based platform aimed to host, display and manage big data on genome annotations in a collaborative manner. This advanced Content Management System (CMS) is currently under development in the Bioinformatics Core. For more information, see | + | |Description=AnnoWiki is a Semantic MediaWiki based platform aimed to host, display and manage big data on genome annotations in a collaborative manner. This advanced Content Management System (CMS) is currently under development in the Bioinformatics Core. For more information, see [http://www.slideshare.net/lucacozzuto/annowiki our poster illustrating the application]. |
|Color=rgba(253, 194, 47, 0.36) | |Color=rgba(253, 194, 47, 0.36) | ||
|Image=annowiki logo.png | |Image=annowiki logo.png | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
|Title=De novo Genome Assembly of Different Fly Species | |Title=De novo Genome Assembly of Different Fly Species | ||
| − | |Description=The Bioinformatics Core collaborates with the group of Yogi Jaeger (CRG) to assemble and annotate the genomes of three non-drosophilid diptera, Clogmia albipunctata, Megaselia abdita, and Episyrphus balteatus. We previously published the de novo transcriptomes of these flies [http://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2164-14-123]. | + | |Description=The Bioinformatics Core collaborates with the group of Yogi Jaeger (CRG) to assemble and annotate the genomes of three non-drosophilid diptera, Clogmia albipunctata, Megaselia abdita, and Episyrphus balteatus. We previously published the de novo transcriptomes of these flies in [http://bmcgenomics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2164-14-123 BMC Genomics, 2013]. |
|Color=rgba(30, 80, 225, 0.26) | |Color=rgba(30, 80, 225, 0.26) | ||
|Image=Screen Shot 2016-05-17 at 12.59.34.png | |Image=Screen Shot 2016-05-17 at 12.59.34.png | ||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
|Title=Mycoplasma Database | |Title=Mycoplasma Database | ||
| − | |Description=MyMpn is | + | |Description=MyMpn is a public resource for studying the human pathogen Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a minimal bacterium causing lower respiratory tract infections. M. pneumonia is also used as a model organism for systems biology studies of unicellular organisms. The Bioinformatics Core designed and developed MyMpn to host and analyze omics-data generated by The Design of Biological Systems Group at the CRG and collaborators at the EMBL and other institutions. For more information, visit the [http://mympn.crg.eu/ MyMpn website]. The database was published in [http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/43/D1/D618 NAR, 2015]. |
|Color=rgba(0, 138, 3, 0.31) | |Color=rgba(0, 138, 3, 0.31) | ||
|Image=MyMpn.png | |Image=MyMpn.png | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
| − | |Title=Melon | + | |Title=Melon Genome |
| − | |Description=Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is a cucurbit with high economic impact and a well-known and appreciated product in Europe. Spain is the fifth world producer and the main exporter. Genoma España | + | |Description=Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is a cucurbit with high economic impact and a well-known and appreciated product in Europe. Spain is the fifth world producer and the main exporter of melon. The governmental foundation Genoma España funded the project "MELONOMICS", to which the Bioinformatics Core contributed by predicting small non-coding RNAs and detecting resistant genes predicted from the genome sequence. For more information, visit https://melonomics.net/. The results were published in [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3406823/ PNAS, 2012]. |
|Color=rgba(255, 149, 38, 0.32) | |Color=rgba(255, 149, 38, 0.32) | ||
|Image=Melonomics2.jpg | |Image=Melonomics2.jpg | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
| − | |Title=Common Bean | + | |Title=Common Bean Genome |
| − | |Description=The Bioinformatics Core collaborated with an international consortium to decode the Mesoamerican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). The findings | + | |Description=The Bioinformatics Core collaborated with an international consortium to decode the genome of the Mesoamerican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). The core contributed by identifying small ncRNAs and annotating genes predicted from the genome sequence. The findings were reported in [http://genomebiology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13059-016-0883-6 Genome Biology, 2016]. |
|Color=rgba(169, 80, 57, 0.43) | |Color=rgba(169, 80, 57, 0.43) | ||
|Image=Bean-01.jpg | |Image=Bean-01.jpg | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
| − | |Title=SuperFly | + | |Title=SuperFly Database |
|Description=SuperFly is a database for the comparative analysis of segmentation gene expression and regulation in dipteran species (flies, midges, and mosquitoes). Currently, it hosts semi-quantitative, spatio-temporal expression data for maternal co-ordinate, and gap genes in three species: the vinegar fly Drosophila melanogaster (Drosophilidae), the scuttle fly Megaselia abdita (Phoridae), and the moth midge Clogmia albipunctata (Psychodidae). The Bionformatics Core developed both the database and the website to collect and display the data. The website can be visited here: http://superfly.crg.eu/. Here the publication: [http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/11/16/nar.gku1142.full.pdf] | |Description=SuperFly is a database for the comparative analysis of segmentation gene expression and regulation in dipteran species (flies, midges, and mosquitoes). Currently, it hosts semi-quantitative, spatio-temporal expression data for maternal co-ordinate, and gap genes in three species: the vinegar fly Drosophila melanogaster (Drosophilidae), the scuttle fly Megaselia abdita (Phoridae), and the moth midge Clogmia albipunctata (Psychodidae). The Bionformatics Core developed both the database and the website to collect and display the data. The website can be visited here: http://superfly.crg.eu/. Here the publication: [http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2014/11/16/nar.gku1142.full.pdf] | ||
|Color=rgba(179, 123, 146, 0.31) | |Color=rgba(179, 123, 146, 0.31) | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
{{ProjectBlock | {{ProjectBlock | ||
|Title=PRGdb 2.0 | |Title=PRGdb 2.0 | ||
| − | |Description=The Plant Resistance Genes database | + | |Description=The Plant Resistance Genes database, [http://prgdb.crg.eu/wiki/Main_Page PRGdb], is a comprehensive resource on resistance genes (R-genes), a major class of genes in plant genomes that convey disease resistance against pathogens. Initiated in 2009, the database has grown more than 6-fold to recently include annotation derived from recent plant genome sequencing projects. Release 2.0 currently hosts useful biological information on a set of 112 known and 104 310 putative R-genes present in 233 plant species and conferring resistance to 122 different pathogens. Moreover, the website has been completely redesigned with the implementation of Semantic MediaWiki technologies, which makes this repository freely accessed and easily edited by any scientists. The Bionformatics Core participated to this project by providing the wiki infrastructure and redesigning the interface. The databased was published in NAR:[http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/41/D1/D1167.long] |
|Color=rgba(0, 199, 75, 0.39) | |Color=rgba(0, 199, 75, 0.39) | ||
|Image=PRG db logo.png | |Image=PRG db logo.png | ||
Revision as of 14:57, 24 August 2016
"Saca La Lengua"
‘Stick Out Your Tongue’ (‘Saca la Lengua’) is a citizen’s science project that aims to study the mouth’s microbiome of a large population of healthy young Spaniards and the microbiome profiles relationship with environmental characteristics and lifestyle. The Bioinformatics Core is involved in processing of the 16S rRNA sequencing data, obtaining microbiome abundance profiles for each individual, setting up a website for the data analysis competition, and teaching students and public about bioinformatics and microbiome analysis. For more information, visit the Saca La Lengua public website.
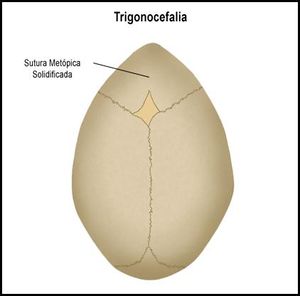
Whole Genome Analysis of an Opitz-C Syndrome Patient
The C syndrome, also known as the Opitz trigonocephaly syndrome, is a malformation syndrome characterized by trigonocephaly, severe mental retardation, hypotonia, variable cardiac defects, redundant skin, and dysmorphic facial features (by Kaname et al., 2007). The Bioinformatics Core collaborates with the University of Barcelona on analysis of the whole genomes of a patient and her parents to detect the putative causative mutations.
Lung Microbiomes of COPD Patients
CRG collaborates with the Hospital San Pau, Hospital Clinic, Hospital del Mar and other institutions in Barcelona on studies of the lung micro biomes of patients affected by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The Bioinformatics Core is part contributes to the project by processing and analyzing of the sequencing data.
AnnoWiki
AnnoWiki is a Semantic MediaWiki based platform aimed to host, display and manage big data on genome annotations in a collaborative manner. This advanced Content Management System (CMS) is currently under development in the Bioinformatics Core. For more information, see our poster illustrating the application.
Wiki-based CMS for Core Facilities
The Bioinformatics Core developed several Semantic MediaWiki LIMSs (Laboratory Information Management System) to manage the laboratory's operations, data flow, and communication with users and external collaborators. One of such LIMS is used by the CRG Proteomics Core and can be accessed at http://proteowiki.crg.eu.
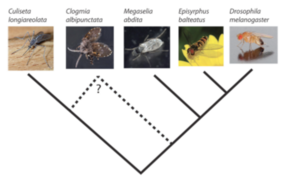
De novo Genome Assembly of Different Fly Species
The Bioinformatics Core collaborates with the group of Yogi Jaeger (CRG) to assemble and annotate the genomes of three non-drosophilid diptera, Clogmia albipunctata, Megaselia abdita, and Episyrphus balteatus. We previously published the de novo transcriptomes of these flies in BMC Genomics, 2013.
Mycoplasma Database
MyMpn is a public resource for studying the human pathogen Mycoplasma pneumoniae, a minimal bacterium causing lower respiratory tract infections. M. pneumonia is also used as a model organism for systems biology studies of unicellular organisms. The Bioinformatics Core designed and developed MyMpn to host and analyze omics-data generated by The Design of Biological Systems Group at the CRG and collaborators at the EMBL and other institutions. For more information, visit the MyMpn website. The database was published in NAR, 2015.
Melon Genome
Melon (Cucumis melo L.) is a cucurbit with high economic impact and a well-known and appreciated product in Europe. Spain is the fifth world producer and the main exporter of melon. The governmental foundation Genoma España funded the project "MELONOMICS", to which the Bioinformatics Core contributed by predicting small non-coding RNAs and detecting resistant genes predicted from the genome sequence. For more information, visit https://melonomics.net/. The results were published in PNAS, 2012.
Common Bean Genome
The Bioinformatics Core collaborated with an international consortium to decode the genome of the Mesoamerican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). The core contributed by identifying small ncRNAs and annotating genes predicted from the genome sequence. The findings were reported in Genome Biology, 2016.
SuperFly Database
SuperFly is a database for the comparative analysis of segmentation gene expression and regulation in dipteran species (flies, midges, and mosquitoes). Currently, it hosts semi-quantitative, spatio-temporal expression data for maternal co-ordinate, and gap genes in three species: the vinegar fly Drosophila melanogaster (Drosophilidae), the scuttle fly Megaselia abdita (Phoridae), and the moth midge Clogmia albipunctata (Psychodidae). The Bionformatics Core developed both the database and the website to collect and display the data. The website can be visited here: http://superfly.crg.eu/. Here the publication: [1]
PRGdb 2.0
The Plant Resistance Genes database, PRGdb, is a comprehensive resource on resistance genes (R-genes), a major class of genes in plant genomes that convey disease resistance against pathogens. Initiated in 2009, the database has grown more than 6-fold to recently include annotation derived from recent plant genome sequencing projects. Release 2.0 currently hosts useful biological information on a set of 112 known and 104 310 putative R-genes present in 233 plant species and conferring resistance to 122 different pathogens. Moreover, the website has been completely redesigned with the implementation of Semantic MediaWiki technologies, which makes this repository freely accessed and easily edited by any scientists. The Bionformatics Core participated to this project by providing the wiki infrastructure and redesigning the interface. The databased was published in NAR:[2]
Iberian Lynx genome project
A total of six research Spanish centers and more than thirty researchers are involved in Lynxgenomics, which aims is the generation of a first map of the Iberian lynx genome (an annotated draft) and of a comprehensive set of markers for genomic analyses in the species. Specialists in genomic and biology have joined forces and knowledge to reach these two aims under EBD's coordination in this project, framed in the Project Zero program FGCSIC 2010 in Endangered Species, and financed by Banco Santander and Fundación General CSIC. More info at http://www.lynxgenomics.eu/